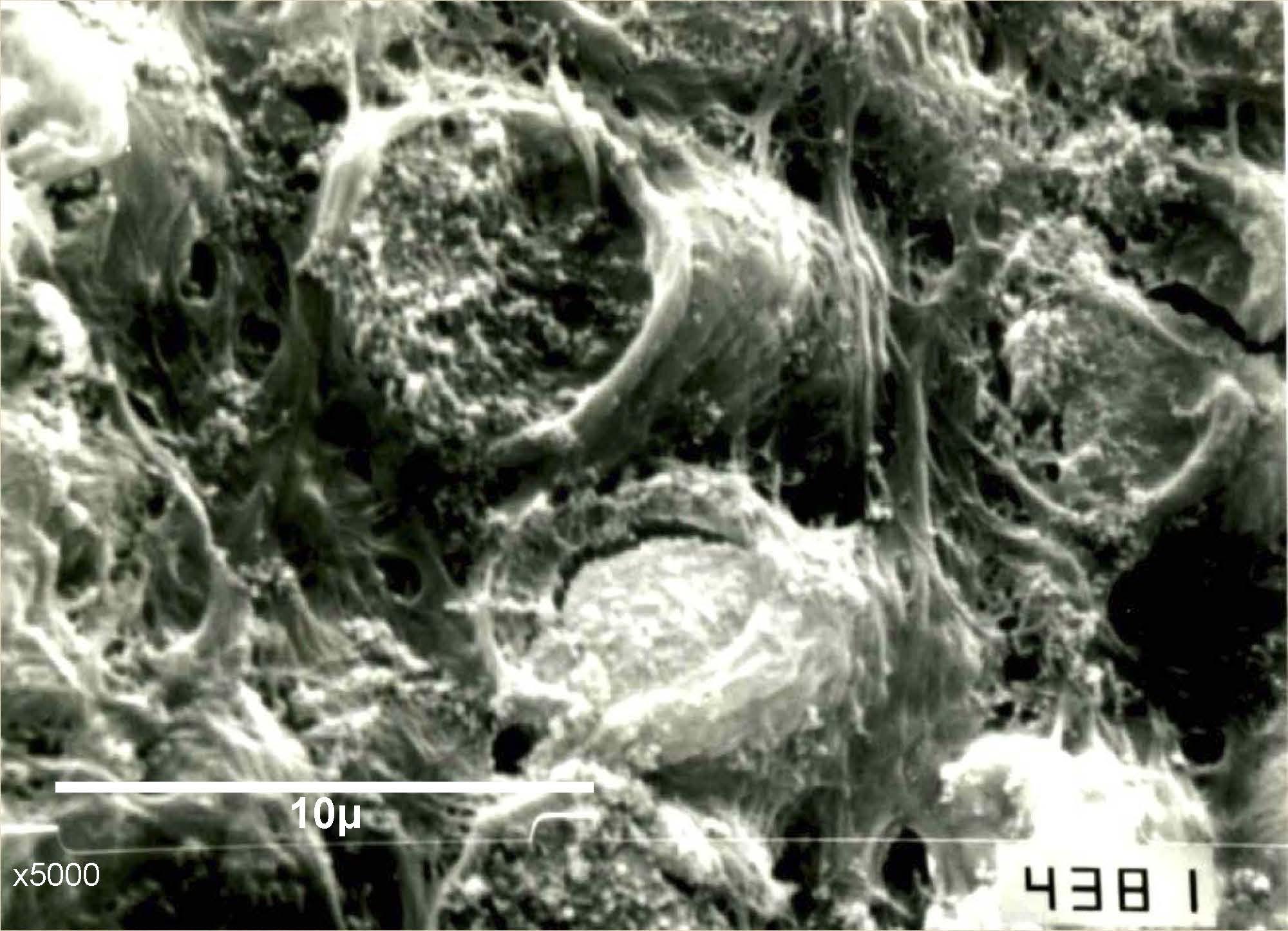
Study of the microstructure on human tooth enamel in relation to microhardness and chemical composition
Keywords:
human tooth enamel, enamel bands, radial enamel, microhardness, chemical compositionAbstract
We compared the microhardness and chemical composition of radial and Hunter-Schreger Bands (HSB) of deciduous and permanent human teeth. Tooth crowns were embedded in acrylic resin. Vickers microhardness was determined in radial and HSB enamel. A qualitative and semiquantitative analysis with energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDS) was carried out for Ca, P and Cl ions. Microhardness values in HSB and radial enamel were 276,5 HV (+/- 34,7) and 360,9 HV (+/- 53,0) respectively in deciduous teeth and 301,4 HV (+/- 28,2) and 344,2 HV (+/- 37,5) in permanent teeth. The chemical composition for Ca, P , Cl in deciduous teeth was, 37,02%,15,1% , 0,41% respectively in radial enamel and 37,42%, 14,99%, 0,23% in HSB enamel. In permanent teeth values were 39,33%, 18,69% and 0,49% in radial enamel and 40,17%, 18,85% and 0,29% in HSB enamel. We conclude that variations in the microhardness values and chemical composition of radial enamel and HSB are related to the organization of the microstructure of prismatic enamel.
Downloads
References
Bhaskar SN. (1986).Histología y Embriología Bucal de Orban. Buenos Aires. 9th ed. Buenos Aires: El Ateneo
Boyde A, Fortelius M. (1986) Development, structure and function of rhinoceros enamel. Zool J Linn Soc (87): 181-214
Braly A, Darnell LA, Mann AB, Teaford MF, Wieths TP. (2007) The effect of prism orientation on the indentation testing of human molar enamel. Arch. Oral Biol. Sep; 52(9):856-60.
Cárdenas JM, Murga HM, Villagrán Rueda S, Cárdenas GM, Gutierrez Cantú F, Guerrero Barrera A. (2010) Distribución de elementos químicos en el esmalte dental. Revista de Ciencias Basicas UJAT. Junio; 9(1): 3–11.
Cuy JL, Mann AB, Livi KJ, Teaford MF, Weihs TP(2002) Nanoindentation mapping of the mechanical properties of human molar tooth enamel. Arch Oral Biol. Apr; 47(4):281-91.
De Menezes Oliveira MA, Torres CP, Gomes-Silva JM, Chinelatti MA, De Menezes FC, Palma-Dibb RG, Borsato MC. (2010) Microstructure and mineral composition of dental enamel of permanent and deciduous teeth. Microsc Res Tech. May; 73(5): 572-7.
Durso G, Abal A. (2008) Variabilidad de la morfología de los prismas del esmalte humano. Acta Microscópica 17: 1-8.
Durso G, Tanevitch A, Batista S, Abal A, Llompart G, Llompart J, Martinez C, Licata L, Perez P. (2013) Estudios sobre la microestructura del esmalte en dientes deciduos. Publicación Informativa y Científica de la Facultad de Odontología UNLP. Junio; 1: 23-28.
Goin F, Durso G, Anselmino C, Batista S, Tanevitch A, Abal A. (2007) Microestructura del esmalte dentario: definiciones y conceptos. RAOA 95 (5): 393-398.
Gomez de Ferraris ME, Campos Muñoz A. (2002) Histología y Embriología Bucodental. 2nd ed. Madrid: Médica Panamericana.
Hedge M, Moany A. (2012) Remineralization of enamel subsurface lesions with casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate: A quantitative energy dispersive X-ray analysis using scanning electron microscopy. An in vitro study. J Conserv.Dent. Jan-Mar; 15(1): 61- 67.
Jiang Y, Spears IR, Macho GA. (2003) An investigation into fractured surfaces of enamel of modern human teeth: a combined SEM and computer visualization study. Arch. Oral Biol. ; 48: 449-457.
Koenigswald W, Clemens W. (1992) Levels of complexity in the microstructure of mammalian enamel and their application in studies of systematics. Scanning Microscopy. 6: 195- 218.
Koenigswald W, Sander P. (1997) Glossary of terms used for enamel microstructures. In Koenigswald W SP, editor. Tooth enamel microstructure. Rotterdam: Balkema;.p. 267-297.
Koenigswald W, Goin F. (2000) Enamel differentiation in South American marsupials and comparision of placental and marsupial enamel. Paleontographica Abt. A.B.; 225: 137-141.
Kunin AA, Evdokimova AY, Moiseeva NS. (2015) Age-related differences of tooth enamel morphochemistry in health and dental caries. EPMA J. Jan 29; 6 (1):3. eCollection 2015.
Lynch C, O´Sullivan V, Dockery P, McGillycuddy C, Sloan A. (2010) Hunter-Schreger Band patterns in human tooth enamel. J Anat. Aug; 217(2): 106-115.
Maas, MC (1991) Enamel structure and microwear: an experimental study of the response of enamel to shearing force. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. May; 85(1): 31-4
Rensberger J. (1997) Mechanical adaptation in enamel. In Koenigswald W SP, editor. Tooth enamel microstructure. Rotterdam: Balkema; p. 227-257.
Shimizu D, Spears IR, Macho GA.(2005) Effect of prism orientation and loading direction on contact stresses in prismatic enamel of primates: implication for interpreting wear patterns. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. Apr; 126(4): 427-34.
Staines M, Robinson WH, Hood JAA. (1981) Spherical indentation of tooth enamel. J Mater Sci. ;16:2551–2556
Tanevitch A, Durso G, Batista S, Abal A, Llompart G, Llompart J, Martínez C, Licata L. (2013) Enamel microstucture of deciduous teeth: Types of enemel and resistance to abrasion. e-Universitas UNR Journal. Vol.1 11(6):1718-22
Ten Cate A (1989) Histología Oral. Desarrollo, estructura y función. Buenos Aires. Médica Panamericana, 2° ed. pp 252-273
Xu HH, Smith DT, Jahanmir S, Romberg E, Kelly JR, Thomson VP, Rekow ED. (1998) Indentation damage and mechanical properties of human enamel and dentin. J Dent Res. Mar; 77(3): 472-80.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
1. Política propuesta para revistas de acceso abierto
Los autores/as que publiquen en esta revista aceptan las siguientes condiciones:
- Los autores/as conservan los derechos de autor y ceden a la revista el derecho de la primera publicación, con el trabajo registrado con la licencia de atribución de Creative Commons, que permite a terceros utilizar lo publicado siempre que mencionen la autoría del trabajo y a la primera publicación en esta revista.
- Los autores/as pueden realizar otros acuerdos contractuales independientes y adicionales para la distribución no exclusiva de la versión del artículo publicado en esta revista (p. ej., incluirlo en un repositorio institucional o publicarlo en un libro) siempre que indiquen claramente que el trabajo se publicó por primera vez en esta revista.
- Se permite y recomienda a los autores/as a publicar su trabajo en Internet (por ejemplo en páginas institucionales o personales) despues del proceso de revisión y publicación, ya que puede conducir a intercambios productivos y a una mayor y más rápida difusión del trabajo publicado.